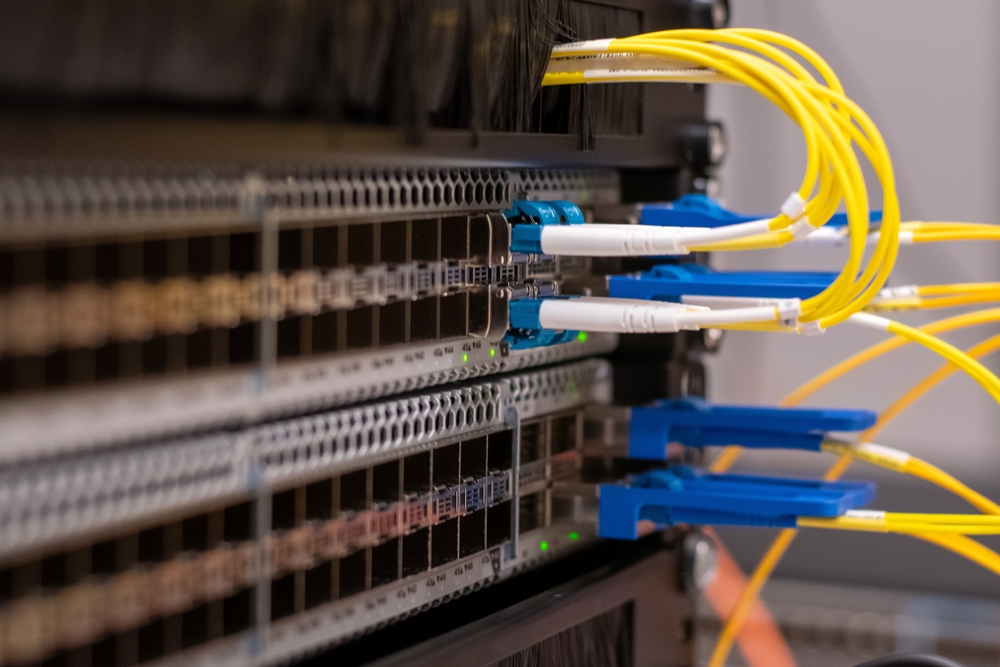
Introduction: What Are Networking Switches?
In the world of IT hardware and networking, one of the most crucial components is the networking switch. These devices play a pivotal role in managing and optimizing network traffic within local area networks (LANs) by directing data between devices in a seamless and efficient manner. Whether you’re setting up a home network or a large-scale enterprise system, understanding networking switches is vital to ensure your network operates smoothly.
A networking switch can be compared to a traffic manager that ensures data packets are sent to the correct destination without unnecessary delays. While switches may seem similar to hubs or routers, they differ significantly in how they manage and forward network traffic.
In this guide, we will explore everything you need to know about networking switches, their different types, and how they impact overall network performance.
Understanding the Role of Networking Switches in IT Hardware
At their core, networking switches are responsible for connecting multiple devices within a network, such as computers, printers, servers, and other hardware components. They operate at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model, where they use MAC addresses to forward data between devices.
In simpler terms, switches act as communication bridges between networked devices. They are designed to manage the data flow in a network by ensuring that data packets are delivered only to the device that requires them, instead of broadcasting to all devices. This minimizes network congestion and improves the efficiency of data transmission.
In addition to connecting devices, networking switches also enable faster and more reliable data transfer. By using high-speed ports and managing traffic efficiently, they play a crucial role in ensuring that large volumes of data can be transmitted without delays or packet loss.
Types of Networking Switches
Networking switches come in various forms, each suited for different networking needs. Understanding the differences between them is essential to selecting the right switch for your environment. Below are the most common types of networking switches:
1. Unmanaged Switches
Unmanaged switches are the most basic type of networking switches, offering plug-and-play functionality with minimal configuration. These switches automatically handle data traffic without any user intervention or network management features.
Unmanaged switches are ideal for small networks or home environments where simplicity and ease of use are key priorities. While they may lack advanced features, they are typically more affordable and are suitable for basic networking tasks where traffic management and monitoring aren’t critical.
2. Managed Switches
Managed switches are more advanced and offer greater control over network traffic. These switches come with built-in software that allows users to monitor, manage, and configure the network in various ways. Managed switches offer features like:
- VLAN Support: Create virtual LANs to segment network traffic and improve security.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Prioritize certain types of traffic (e.g., video conferencing) to ensure optimal performance.
- Port Mirroring: Monitor traffic on specific ports for troubleshooting or security purposes.
- Redundancy and Failover: Provide network reliability in case of switch failure by enabling multiple network paths.
For organizations that require better network control, security, and performance, managed switches are the ideal choice. They are commonly used in enterprise environments where network performance and uptime are critical.
3. Smart Switches
Smart switches combine features from both unmanaged and managed switches. They offer some management capabilities, such as basic VLAN support and QoS settings, but don’t provide the full range of options that managed switches offer. Smart switches are often more affordable than fully managed switches, making them a good option for businesses that need more control than unmanaged switches but don’t require all the features of high-end managed switches.
Key Features of Networking Switches
When selecting a networking switch for your setup, it’s essential to consider several features to ensure optimal performance. Here are some of the most important factors to look for:
1. Port Density
Port density refers to the number of ports available on a switch. This can vary from a few ports to several dozen, depending on the type and size of the switch. When choosing a switch, consider the number of devices you plan to connect and ensure it has enough ports to accommodate them.
Some switches also offer stackable ports, allowing you to connect multiple switches together, expanding the network without requiring additional network infrastructure.
2. Speed and Bandwidth
Networking switches come with varying speeds, typically ranging from 1Gbps (Gigabit Ethernet to 10Gbps (10-Gigabit Ethernet) and even up to 100Gbps in high-end switches. The speed of the switch is crucial for ensuring that data can be transmitted quickly, especially in environments where large files or data-intensive applications are in use.
For most home networks and small businesses, Gigabit Ethernet switches are sufficient. However, for high-performance needs, such as data centres or large enterprises, 10Gbps switches may be necessary.
3. PoE (Power over Ethernet)
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a feature that allows networking devices like IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points to receive both power and data over a single Ethernet cable. This eliminates the need for separate power supplies and simplifies the installation process. For businesses looking to integrate PoE-enabled devices into their network, choosing a PoE switch is a smart choice.
4. Network Security Features
As cyber threats continue to evolve, network security becomes a top priority for businesses. Many managed switches come with built-in security features, such as:
- Port Security: Limits access to the network based on the MAC address of the device connected to a port.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): Defines which devices can access specific parts of the network based on IP addresses or other criteria.
- 802.1X Authentication: Requires devices to authenticate themselves before accessing the network.
These security features help safeguard sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access to the network.
5. Quality of Service (QoS)
Quality of Service (QoS) is a feature that prioritizes specific types of traffic over others to ensure that mission-critical applications, such as VoIP or video streaming, receive the necessary bandwidth. QoS ensures that these applications function smoothly, even in networks with high levels of traffic.
How Networking Switches Improve Network Performance
A networking switch plays a pivotal role in improving the performance of any network. Here’s how:
-
Efficient Data Forwarding: Switches use MAC addresses to forward data only to the destination device, reducing unnecessary traffic and preventing network congestion. This leads to faster data transfers and a more responsive network.
-
Full-Duplex Communication: Switches enable full-duplex communication, allowing devices to send and receive data simultaneously. This increases network efficiency and speeds up data transmission.
-
Bandwidth Management: With features like QoS, switches can prioritize high-bandwidth applications, ensuring that critical tasks receive the necessary resources without delay.
-
Reduced Collisions: Switches reduce data collisions that occur in traditional hubs, where multiple devices share the same bandwidth. With dedicated communication channels for each device, switches ensure a more stable and high-performance network.
Selecting the Right Networking Switch for Your Needs
Choosing the right networking switch depends on several factors, including the size of your network, the number of devices, and the specific performance requirements. Here’s a quick guide to help you make an informed decision:
- For home networks, an unmanaged switch with Gigabit Ethernet speeds should suffice.
- For small businesses, a smart switch or managed switch may be needed for additional control and security.
- For large enterprises or data centres, invest in high-speed, managed switches with PoE, security features, and redundancy options to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Conclusion: Why Networking Switches Matter
Networking switches are integral components of computer hardware that ensure reliable and efficient communication between devices. Whether you are setting up a small home network or managing a complex enterprise-level infrastructure, understanding the role of networking switches is essential for achieving optimal performance.
By selecting the right switch with the necessary features, such as high-speed ports, PoE support, and security functionalities, you can enhance your network’s efficiency, reliability, and scalability. As your network grows, having a well-designed networking infrastructure with the right switches will ensure that your data continues to flow smoothly and securely, enabling you to get the most out of your IT hardware investments.
Related Posts
Top WooCommerce Mini Cart Design Tips for 2024
Did you know that a well-designed mini cart can skyrocket…

The Recruitment Labyrinth: Finding Your Way to the Best Hires
Recruitment in today's fast-paced world can feel like navigating a…

Oppo A1 Pro 5G Price and Features in Pakistan: A Budget Winner
The Oppo A1 Pro 5G has swiftly gained attention in…

